Sensory restoration by epidural stimulation of the lateral spinal cord in upper-limb amputees
Abstract
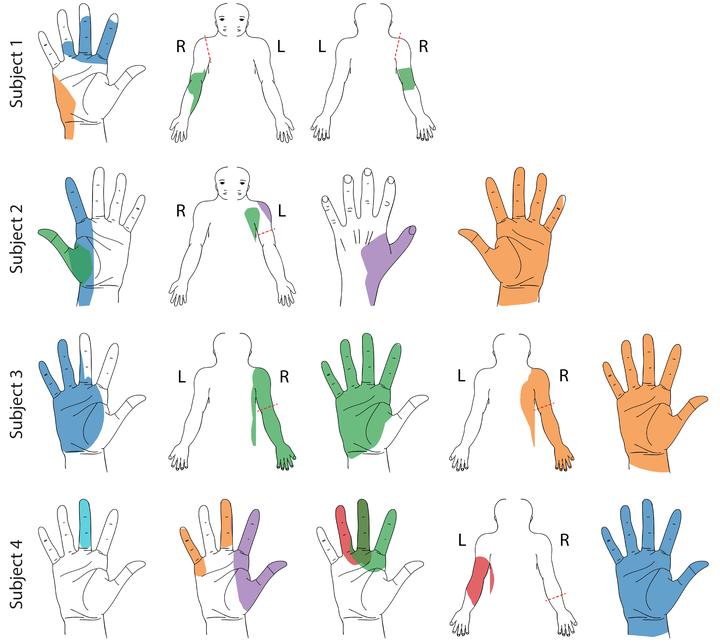
Restoring somatosensory feedback to people with limb amputations is crucial to improve prosthetic control. Multiple studies have demonstrated that peripheral nerve stimulation and targeted reinnervation can provide somatotopically relevant sensory feedback. While effective, the surgical procedures required for these techniques remain a major barrier to translatability. Here, we demonstrate in four people with upper-limb amputation that epidural spinal cord stimulation (SCS), a common clinical technique to treat pain, evoked somatosensory percepts that were perceived as emanating from the missing arm and hand. Over up to 29 days, stimulation evoked sensory percepts in consistent locations in the missing hand regardless of time since amputation or level of amputation. Evoked sensations were occasionally described as naturalistic (e.g. touch or pressure), but were often paresthesias. Increasing stimulus amplitude increased the perceived intensity linearly, without increasing area of the sensations. These results demonstrate the potential of SCS as a tool to restore somatosensation after amputations.